
Animals have been at the heart of human life for centuries, playing pivotal roles in shaping economies worldwide. From being essential components of agricultural systems to driving major sectors like tourism and research, animals contribute to economic activities in ways that extend far beyond food production. In this article, we will explore how animals shape economies globally, focusing on agriculture, livestock, wildlife tourism, pharmaceuticals, and much more.
Advertisement
1. Introduction to Animals and the Economy
Advertisement
Animals have been integral to human societies, providing essential resources and services that support various sectors. Whether they are part of our food systems, assist in transportation, contribute to industry and commerce, or drive cultural and recreational activities, animals play a major role in boosting economic development. In many parts of the world, the livestock sector, which is deeply rooted in animal agriculture, is one of the most important contributors to the economy.
Advertisement
2. The Backbone of Many Economies

Advertisement
In agriculture, animals are foundational. Livestock farming includes the raising of animals for food, such as cows, pigs, chickens, goats, and sheep, and for other products such as wool, leather, and hides. This sector provides raw materials for the food industry, from meat and dairy products to eggs and honey, which support both local markets and global trade.
Advertisement
3.Economic Impact of Livestock

Advertisement
The livestock sector not only provides food but also creates jobs for millions globally. It supports industries such as feed production, veterinary services, transport, and retail. It generates substantial revenue for countries that are major producers of meat, dairy, wool, and other animal-based products. For instance, countries like the United States, Brazil, and Australia are leaders in livestock production and export, driving economic growth in their regions.
Advertisement
4.Animal Products in Manufacturing

Advertisement
Beyond food, animals provide materials used in various manufacturing industries. Leather, wool, and silk are used to make clothing, furniture, and accessories. Animal-based products are also found in cosmetics, medicines, and even industrial equipment. For many developing countries, animal products are crucial to their economies.
Advertisement
5.Dairy and Meat Production: A Growing Industry

Advertisement
The dairy and meat production industries have massive economic implications. The global demand for beef, chicken, pork, and dairy products continues to rise, contributing significantly to agricultural economies. With rising populations and increasing consumer incomes, particularly in emerging markets, the demand for animal protein is expected to continue growing.
Advertisement
6.Meat Production

Advertisement
Meat production, including beef, chicken, and pork, is a primary contributor to the global economy. Large-scale industrial farming and smaller family-owned operations alike help to meet the global demand for meat. Meat production is not only a key source of food but also a major employer and driver of rural economies in many parts of the world. Countries like Argentina, the U.S., and China are major players in this sector.
Advertisement
7.Dairy Production

Advertisement
Dairy farming is another vital component of the global economy. It provides essential products such as milk, cheese, butter, and yogurt, which are consumed worldwide. The dairy industry supports numerous supply chains, from milk production to processing and distribution. For many economies, especially in Europe, North America, and Oceania, dairy farming plays a crucial role in sustaining rural livelihoods.
Advertisement
8. A Small Industry with Big Economic Benefits

Advertisement
Beekeeping, or apiculture, is another industry that highlights the economic contributions of animals. Bees are essential for pollinating many crops, and they also produce honey, beeswax, and other valuable products. Honey production alone is a billion-dollar global industry, with many countries relying on bees for both agricultural productivity and income from bee-related products.
Advertisement
9.Pollination Services

Advertisement
Bees are perhaps best known for their role in pollination. They contribute to the growth of countless plant species, including many crops that humans rely on for food. The value of pollination services is estimated to be worth billions of dollars globally, as it boosts crop yields and supports the agriculture sector. Without bees and other pollinators, the global food supply would be significantly impacted.
Advertisement
10.Honey and Byproducts

Advertisement
In addition to their pollination services, bees also contribute directly to the economy through honey production. Honey is used in a variety of products, from food and beverages to cosmetics and medicine. Beekeeping provides employment and income opportunities, especially in rural areas, making it an important component of agricultural economies.
Advertisement
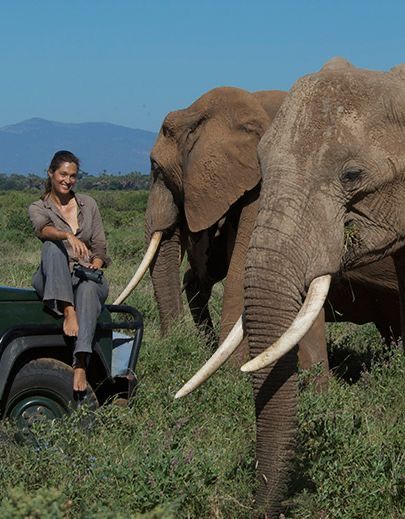
11.The Role of Animals in Wildlife Tourism

Advertisement
Wildlife tourism is a booming sector, contributing significantly to the economy of many countries. Animals, both terrestrial and marine, are the main attraction in safaris, national parks, wildlife reserves, and eco-tourism destinations. Countries with rich biodiversity, such as Kenya, Tanzania, South Africa, and Costa Rica, rely heavily on wildlife tourism as a source of income.
Advertisement
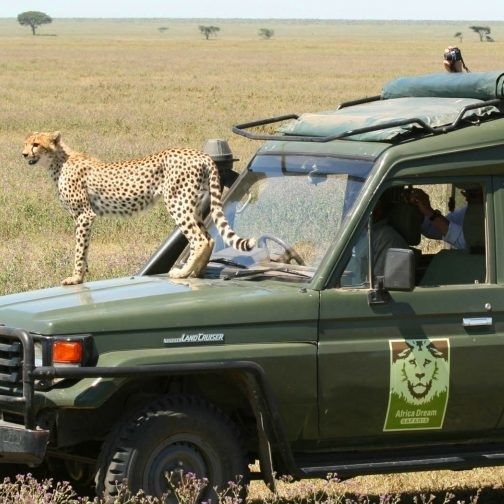
12.Safari Tourism

Advertisement
In countries like Kenya and Tanzania, safaris are one of the primary sources of tourism revenue. Tourists flock to these regions to witness wildlife in its natural habitat, and many businesses rely on this influx of visitors to sustain their operations. From game reserves to national parks, wildlife tourism plays an essential role in driving local economies by generating income through park entrance fees, tour operators, hotels, and local businesses.
Advertisement
13.Marine and Coastal Tourism

Advertisement
Marine life also plays a key role in tourism, particularly in coastal regions. Activities such as whale watching, dolphin tours, and coral reef diving attract millions of tourists every year. These animals not only provide educational and recreational experiences but also help support coastal economies by creating jobs in hospitality, tour guiding, and conservation efforts.
Advertisement
14.The Economic Value of Aquaculture and Fisheries

Advertisement
Aquaculture, or fish farming, has become an essential industry in providing protein to the global population. Fish and seafood are key components of diets around the world, and the fishing industry, both wild-caught and farmed, generates billions of dollars annually. Aquaculture, in particular, is a rapidly growing sector that contributes to food security and job creation.
Advertisement
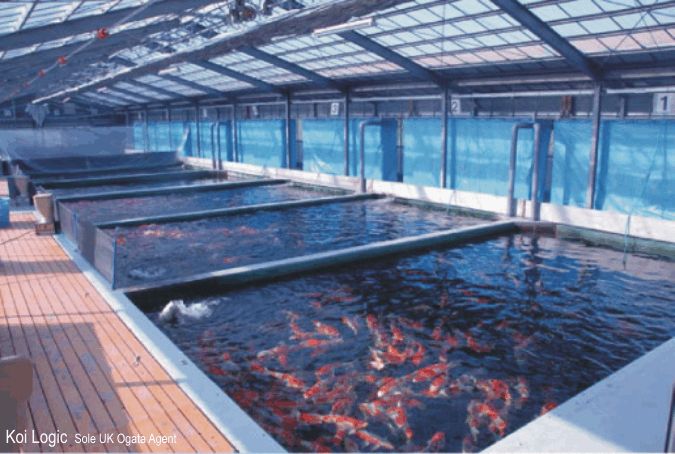
15.Fish Farming

Advertisement
Fish farming has become an essential part of the global food supply. With increasing demand for seafood, especially in countries with growing populations, the aquaculture industry plays a vital role in meeting these needs. Fish farming generates income, provides jobs, and supports international trade, especially in regions such as Asia, where aquaculture is a dominant industry.
Advertisement
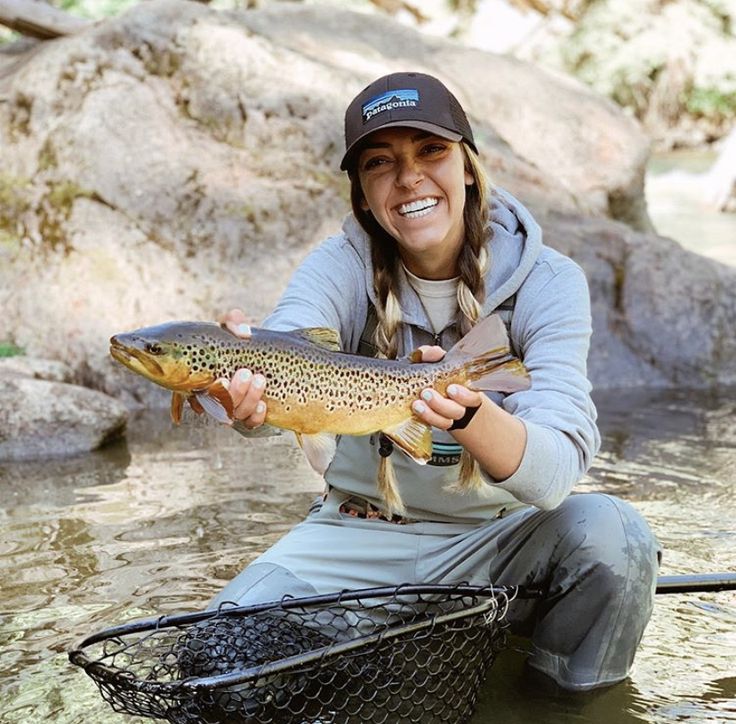
16.Wild Fisheries

Advertisement
Wild fisheries also contribute significantly to the economy. The global fishing industry, which includes commercial and artisanal fishing, provides food for millions of people, both domestically and through export. Many coastal communities depend on fishing as a primary source of income, and the global seafood market supports jobs in fishing, processing, and distribution.
Advertisement
17.Animal Research and Pharmaceuticals: Advancements in Medicine

Advertisement
The role of animals in research and medicine is another major contribution to the global economy. Animal testing has led to the development of vaccines, treatments, and diagnostic tools that have saved millions of lives worldwide. The pharmaceutical industry relies heavily on animals for preclinical testing and the development of new drugs and therapies.
Advertisement
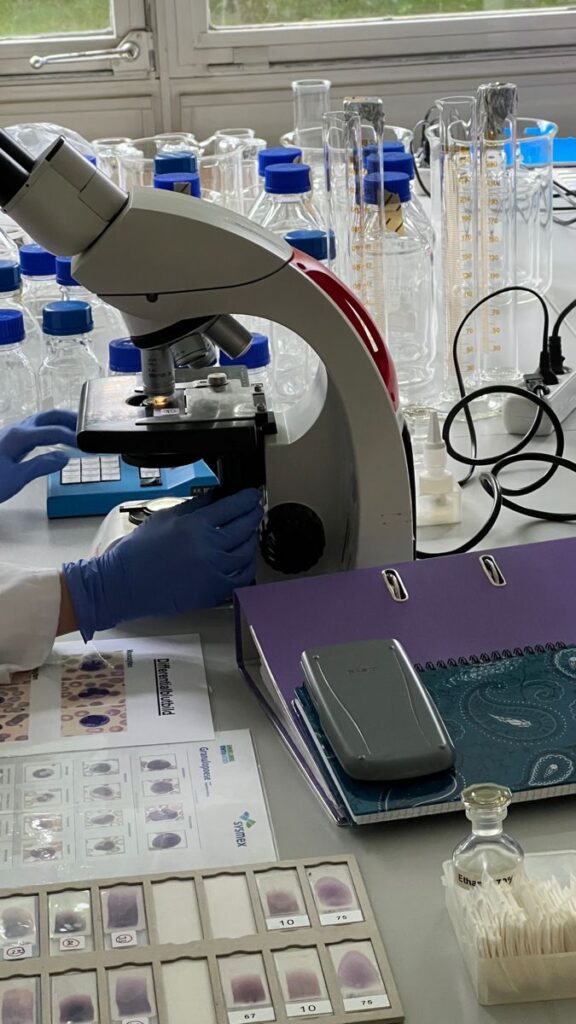
18.Biomedical Research
Advertisement
Animals, including mice, rats, and primates, are essential in medical research, where they help scientists study diseases, test new drugs, and understand human biology. Animal research has been instrumental in the development of life-saving treatments for conditions such as cancer, diabetes, and heart disease. While animal testing remains controversial, its contribution to medical advancements cannot be denied.
Advertisement
19.Veterinary Pharmaceuticals

Advertisement
Animals also play a significant role in the veterinary pharmaceutical industry. From vaccines for livestock to medications for pets, the veterinary sector supports the health of both domestic and wild animals. The economic value of the veterinary industry is substantial, as it includes the production and sale of pharmaceuticals, animal healthcare products, and services.
Advertisement
20. Animals in Education and Research Institutions

Advertisement
Animals are crucial in education and research institutions, where they play a significant role in training future generations of scientists, veterinarians, and biologists. From university research labs to government-funded programs, animals are used in research that benefits both human and animal health. These studies often lead to innovations in biotechnology, medicine, and environmental sciences.
Advertisement
21.Education and Training
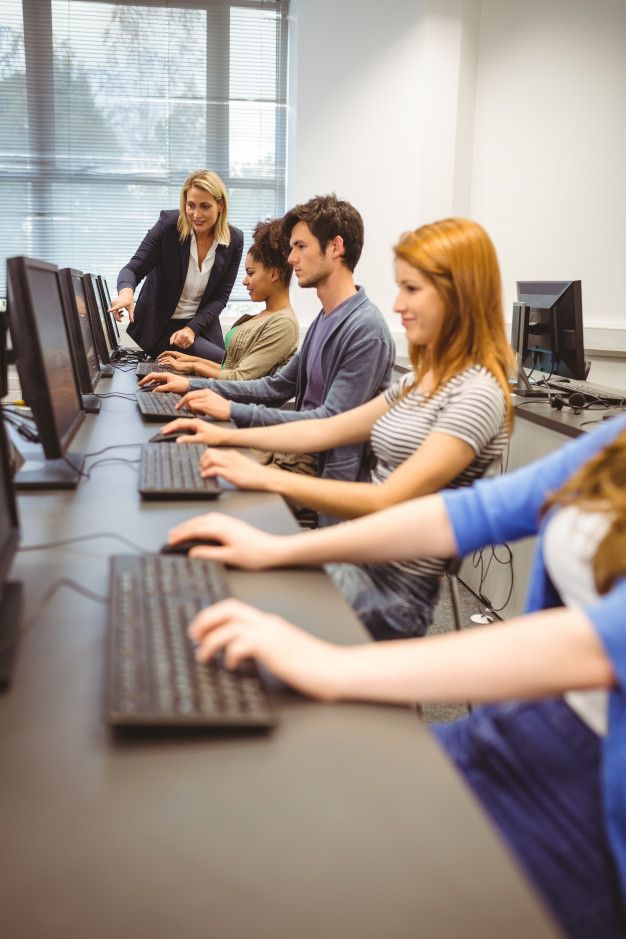

Advertisement
In universities and research institutions, animals are used to teach students about biology, medicine, and veterinary sciences. This hands-on experience is essential for building expertise and fostering future scientific leaders. The economic impact of research institutions is vast, as they contribute to job creation, technological innovation, and the development of cutting-edge therapies.
Advertisement
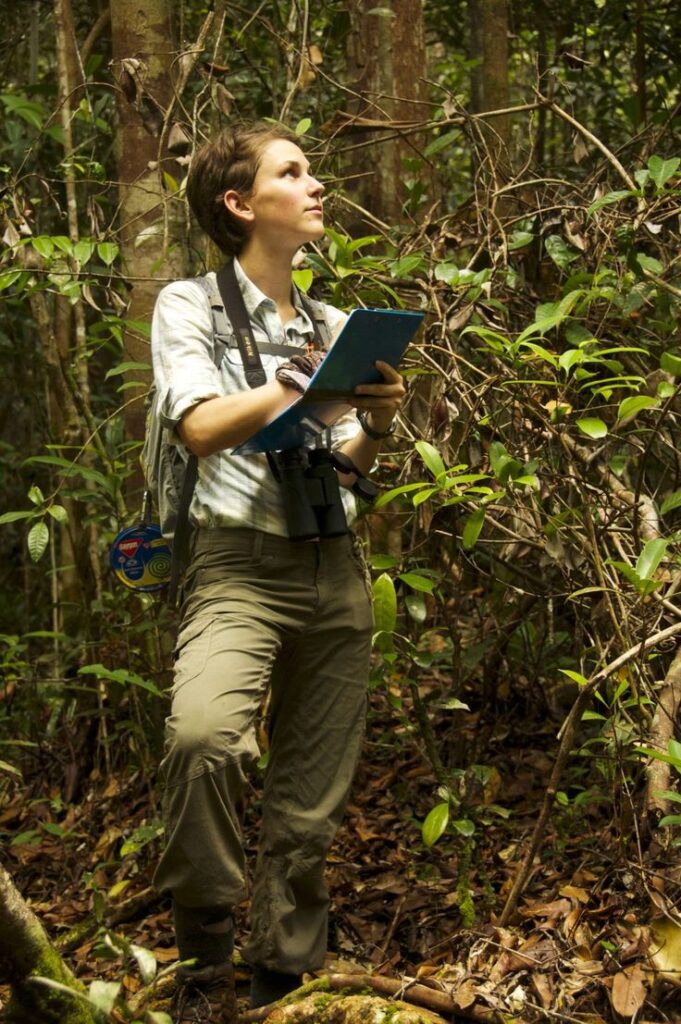
22.Conservation Research

Advertisement
Animal research also plays a vital role in conservation efforts. By studying the behaviors, populations, and health of endangered species, researchers are able to develop strategies to protect animals from extinction. These efforts often involve local communities and provide opportunities for eco-tourism, sustainable agriculture, and biodiversity conservation.
Advertisement
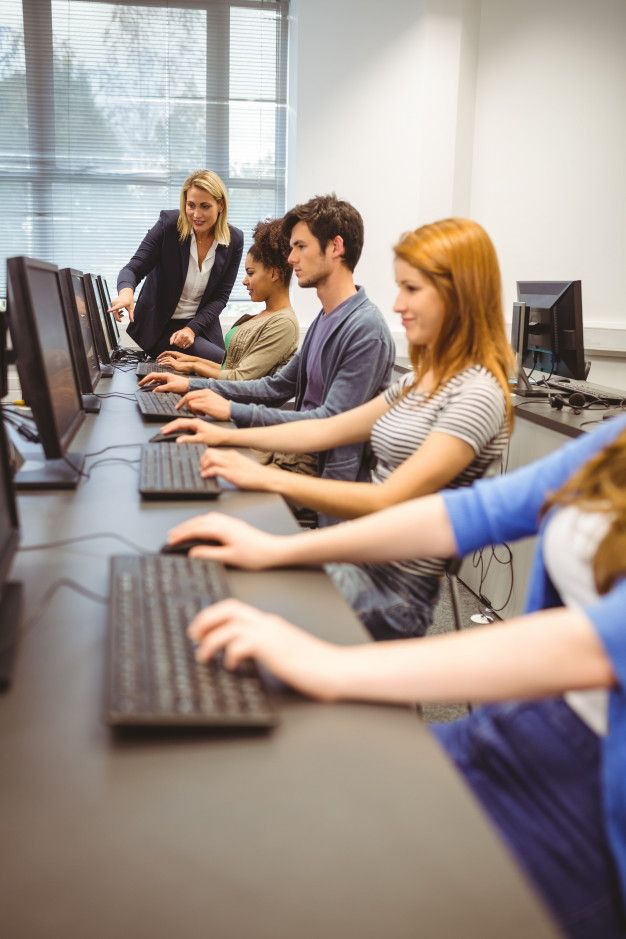
23. Ethical and Sustainable Practices: The Future of Animal Contributions

Advertisement
As concerns about animal welfare and sustainability continue to grow, there is a rising push for more ethical and sustainable practices in industries that rely on animals. This includes adopting cruelty-free farming methods, supporting wildlife conservation, and minimizing the environmental impact of animal-based industries.
Advertisement
24.Sustainable Farming

Advertisement
Sustainable farming practices aim to reduce the negative environmental impact of animal agriculture while improving animal welfare. These practices include rotational grazing, free-range farming, and the reduction of factory farming, which has been criticized for its environmental and ethical concerns.
Advertisement
25.Wildlife Conservation and Sustainable Tourism

Advertisement
Sustainable wildlife tourism focuses on preserving ecosystems and ensuring that animals are protected from harm. Ethical tourism practices include promoting responsible travel, supporting wildlife protection initiatives, and educating tourists on conservation efforts.
Advertisement
26.Introduction to Animals and the Economy

Advertisement
Animals have been integral to human societies, providing essential resources and services that support various sectors. Whether they are part of our food systems, assist in transportation, contribute to industry and commerce, or drive cultural and recreational activities, animals play a major role in boosting economic development. In many parts of the world, the livestock sector, which is deeply rooted in animal agriculture, is one of the most important contributors to the economy.
Advertisement
27. Dairy and Meat Production: A Growing Industry

Advertisement
The dairy and meat production industries have massive economic implications. The global demand for beef, chicken, pork, and dairy products continues to rise, contributing significantly to agricultural economies. With rising populations and increasing consumer incomes, particularly in emerging markets, the demand for animal protein is expected to continue growing.
Advertisement
